« Recommends that pre-filled syringes should be used wherever possible. » (1)
recommends, « minimise bedside preparation of intravenous medications and replace with procured and centrally prepared « ready-to-administer » or « ready-to-use » medications wherever possible. » (2)
« Experts suggest that anaesthetists preferentially use pre-filled syringes for occasional use medications when they have them, rather than preparing these medications in advance in conventional syringes, to reduce the environmental impact of general anaesthesia » (translated) (3)
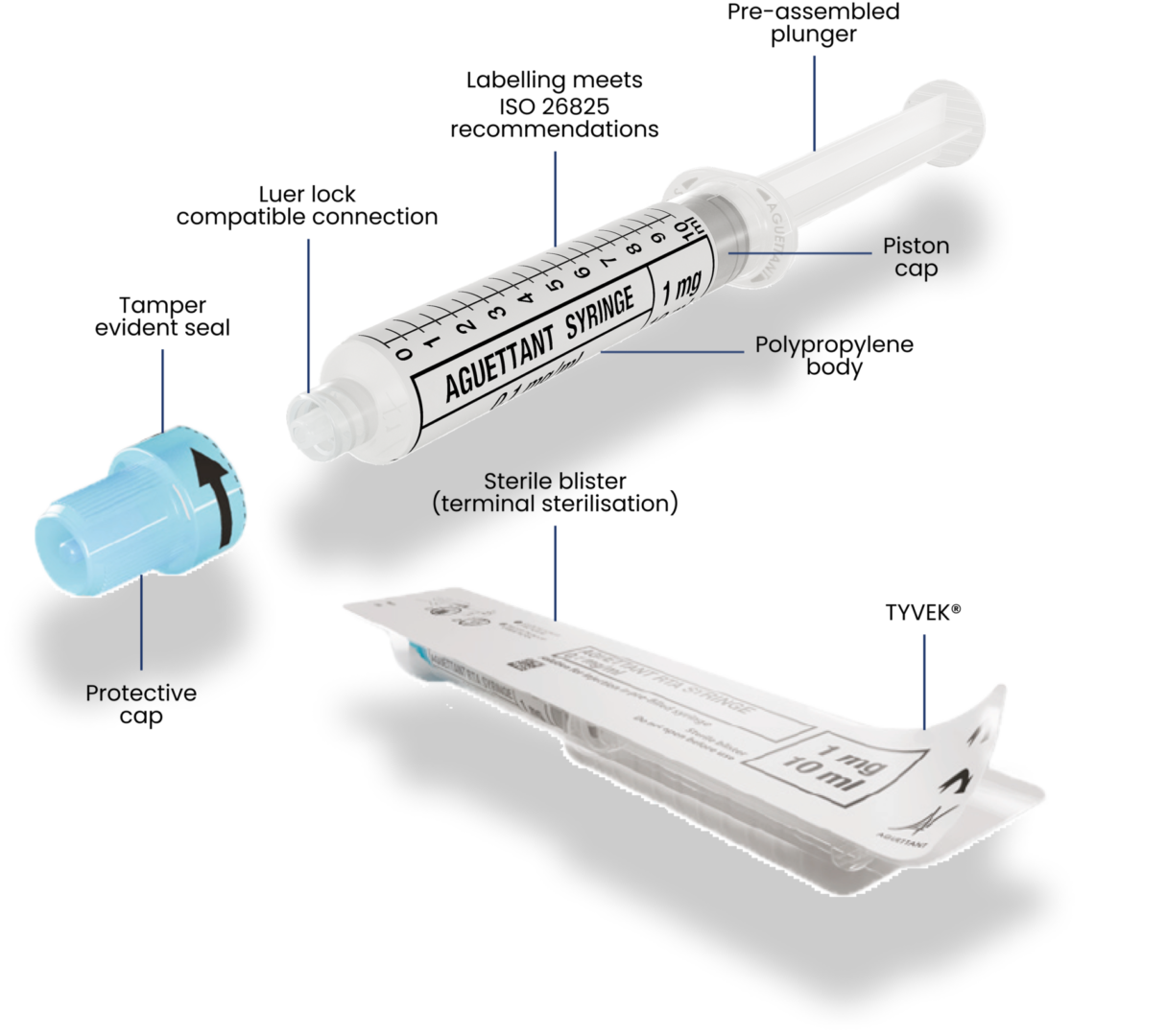
Our polypropylene syringes are delivered pre-filled and ready-to-use in sterile packaging.
We strive to design innovative, ready-to-administer solutions to prevent medication errors, especially in emergency situations. (4)
Thirteen drugs for injection in pre-filled syringes already exist and others are under development.
When fast administration is essential, hand-preparing drugs at the bedside can result in delays in treatment. (5)
Ready-to-use pre-filled syringes eliminate preparation time, making them a suitable solution for emergency situations.
Use of pre-filled syringes eliminates needle-stick and cut injuries when opening glass ampoules. (7)
Up to 86% of injectable drugs prepared in advance in the operating theater and intensive care are discarded at the end of the day. (8)
Considering all components used in the preparation steps of ampoules (syringe, drug, needle, pad, diluent...etc), pre-filled syringes could reduce your overall plastic use and the amount of waste you send to incinerators.